Weather Insider: How tornadoes get their ratings and what they mean
After strong winds and/or storm damage is reported to the National Weather Service, a team is dispatched to survey the area. The teams will then assess the damage and determine if a tornado can be confirmed as well as its potential rating.
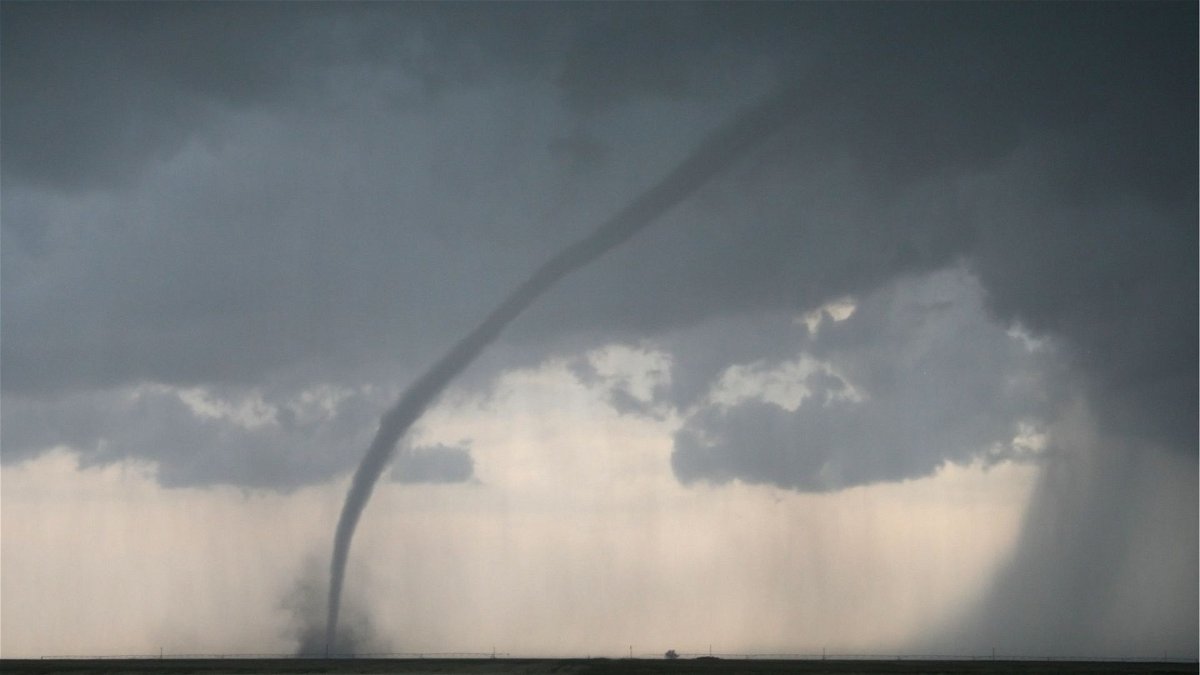

The Enhanced Fujita (EF) scale works by inferring tornadic wind speeds from damage caused by the tornado. Based on certain damage indicators and factors like how well a structure was built, the National Weather Service can determine how fast the tornado's winds were to cause the damage.
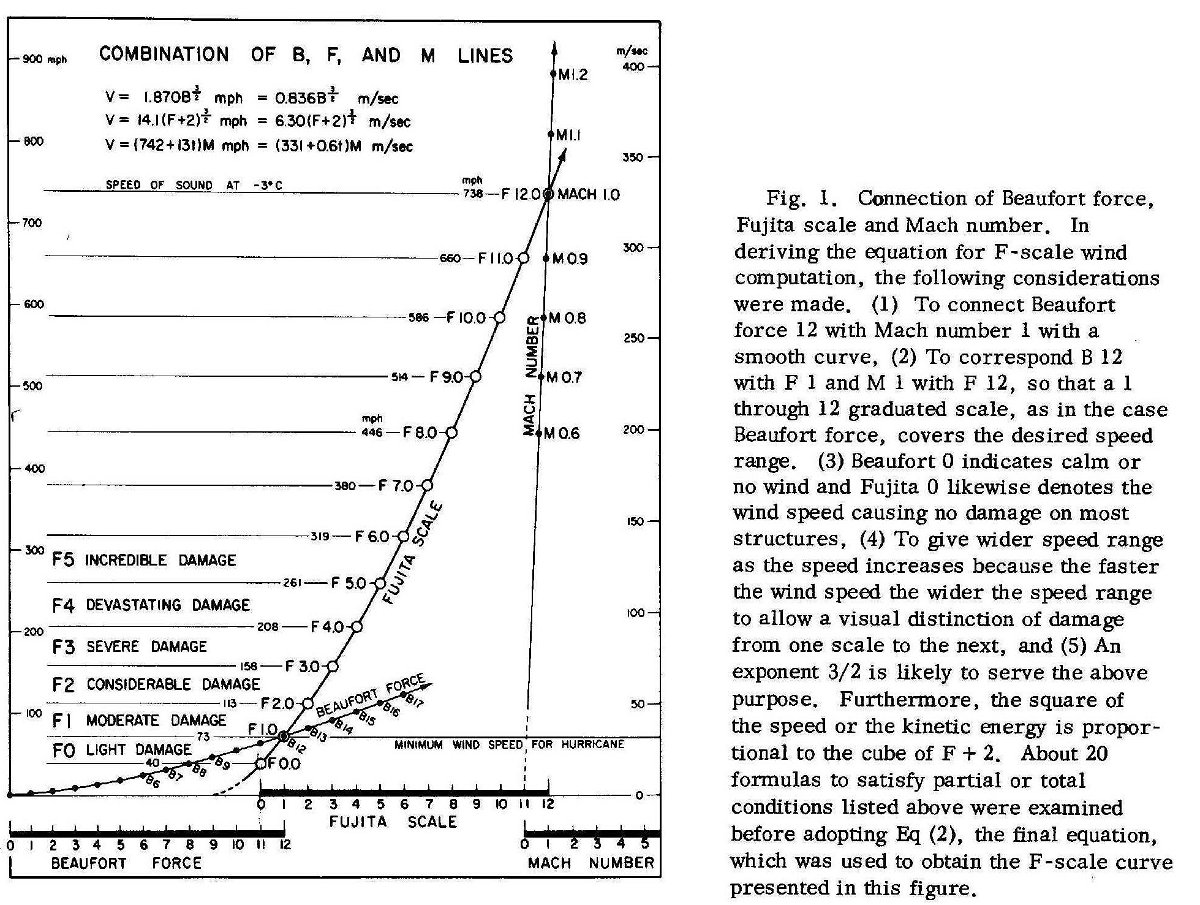
Based on the winds inferred/damage observed, the National Weather Service will assign the tornado a rating from EF-0 to EF-5, with EF-5 damage representing the complete devastation of a structure or area.
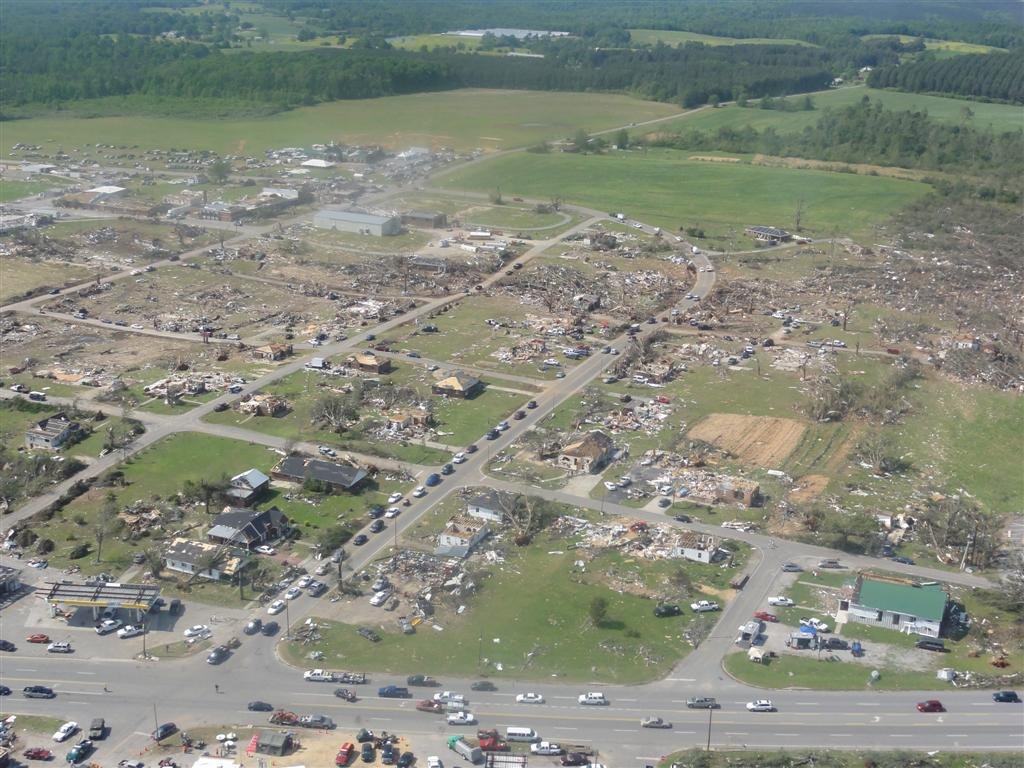

As with any ratings guideline, the system isn't perfect. Since tornadoes are assessed based on the damage they cause, there could theoretically be an exceptionally powerful tornado, but if it only passes over open prairie, it will end up with a rating of EF-0 or EF-1.
