Monkeypox

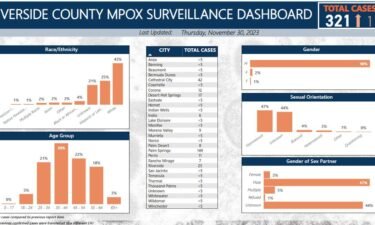
Riverside County MPX Case Data
Riverside County MPX Vaccine Data
Monkeypox Resources
There are a number of ways to prevent the spread of monkeypox, including:
- Always talk to your sexual partner/s about any recent illness and be aware of new or unexplained sores or rashes on your body or your partner’s body, including on the genitals and anus
- Avoiding close contact, including sex, with people with symptoms like sores or rashes
- Practicing good hand hygiene
- People who become infected should isolate until their symptoms are improving or have gone away completely. Rash should always be well covered until completely healed.
- Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) (like a mask, gown, and gloves) when caring for others with symptoms
- Avoiding contact with infected materials contaminated with the virus
- Avoiding contact with infected animals
Source: Riverside County Department of Public Health
Monkeypox is generally spread through intimate skin-to-skin contact, resulting from infectious rashes and scabs, though respiratory secretions and bodily fluids exchanged during extended physical episodes, such as sexual intercourse, can also lead to transmission, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control.
Symptoms include fresh pimples, blisters, rashes, fever and fatigue. There is no specific treatment. People who have been infected with smallpox, or have been vaccinated for it, may have immunity to monkeypox.
People with symptoms are urged to visit a medical provider, cover the rash area with clothing, wear a mask and avoid close or skin-to-skin contact with others.
The CDC particularly recommends those steps for people who recently traveled to an area where monkeypox cases have been reported or who have had contact with a confirmed or suspected monkeypox case.
A full list of countries that have confirmed monkeypox cases is available at wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/notices/alert/monkeypox.
A state-by-state tally of cases is available at www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/response/2022/us-map.html.
Link: CDC’s tips for preventing exposure to Monkeypox.